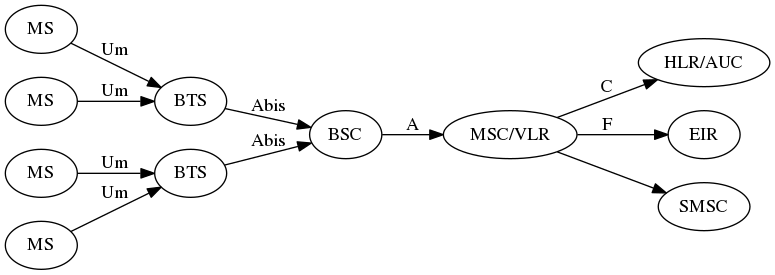
Until 2009 the situation looked like this:
In 2008, some people started to write FOSS for GSM
bs11-abis to bsc_hack to OpenBSC
Mobile Station (your phone)
Base Transceiver Station, consists of 1..n TRX
Transceiver for one radio channel, serves 8 TS
Timeslots in the GSM radio interface; each runs a specific combination of logical channels
Base Station Controller
Mobile Switching Center; Terminates MM + CC Sub-layers
Home Location Register; Subscriber Database
SMS Service Center
Link Access Protocol, D-Channel. Like LAPD in ISDN
Radio Resource (establish/release dedicated channels)
Mobility Management (registration, location, authentication)
Call Control (voice, circuit switched data, fax)
Connection Management
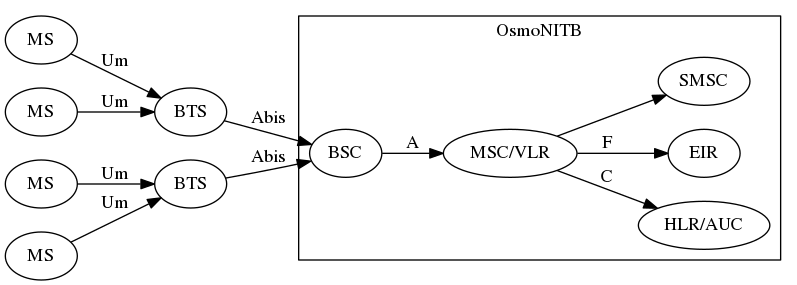
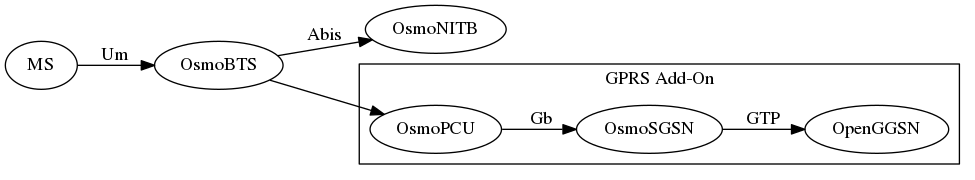
which further reduces to the following minimal setup:
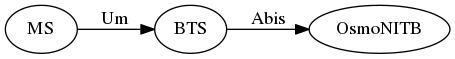
So our minimal setup is a Phone, a BTS and OsmoNITB.
We assume a sysmoBTS in the following tutorial
osmo-bts-sysmo: BTS family by sysmocom
osmo-bts-trx: Used with OsmoTRX + general-purpose SDR
osmo-bts-octphy: Octasic OCTBTS hardware / OCTSDR-2G PHY
osmo-bts-litecell15: Nutaq Litecell 1.5 hardware/PHY
configure terminal and interactively change it
/etc/osmocom/osmo-bts.cfg as
described in the following slide
bts 0
band DCS1800 <1>
ipa unit-id 1801 0 <2>
oml remote-ip 192.168.100.11 <3>the GSM frequency band in which the BTS operates
the unit-id by which this BTS identifies itself to the BSC
the IP address of the BSC (to establish the OML connection towards it)
|
Note
|
All other configuration is downloaded by the BSC via OML. So most BTS settings are configured in the BSC/NITB configuration file. |
osmo-nitb executable built from the openbsc
source tree / git repository
git clone && autoreconf -fi && ./configure && make install
libosmo* dependencies are required first…)
network
network country code 1 <1>
mobile network code 1 <2>
shot name Osmocom <3>
long name Osmocom
auth policy closed <4>
encryption a5 0 <5>MCC (Country Code) e.g. 262 for Germany; 1 == Test
MNC (Network Code) e.g. mcc=262, mnc=02 == Vodafone; 1 == Test
Operator name to be sent to the phone after registration
Only accept subscribers (SIM cards) explicitly authorized in HLR
Use A5/0 (== no encryption)
network
bts 0
type sysmobts <1>
band DCS1800 <2>
ms max power 33 <3>
periodic location update 6 <4>
ip.access unit_id 1801 0 <5>
codec-support fr hr efr amr <6>type of the BTS that we use (must match BTS)
frequency band of the BTS (must match BTS)
maximum transmit power phones are permitted (33 dBm == 2W)
interval at which phones should send periodic location update (6 minutes)
Unit ID of the BTS (must match BTS)
Voice codecs supported by the BTS
network
bts 0
trx 0
arfcn 871 <1>
max_power_red 0 <2>
timeslot 0
phys_chan_config CCCH+SDCCH4 <3>
timeslot 1
phys_chan_config TCH/F <4>
...
timeslot 7
phys_chan_config PDCH <5>The RF channel number used by this TRX
The maximum power reduction in dBm. 0 = no reduction
Every BTS needs need one timeslot with a CCCH
We configure TS1 to TS6 as TCH/F for voice
We configure TS6 as PDCH for GPRS
→ let’s check if we can perform LOCATION UPDATE on our own network
logging level mm info
→ should show LOCATION UPDATE request / reject / accept
show *)
*#100# from any registered MS to obtain own number
show commands)
Program |
Telnet Port |
OsmoPCU |
4240 |
OsmoBTS |
4241 |
OsmoNITB |
4242 |
OsmoSGSN |
4245 |
? and list commands
show subsciber to display data about subscriber:
OpenBSC> show subscriber imsi 901700000003804
ID: 12, Authorized: 1
Extension: 3804
LAC: 0/0x0
IMSI: 901700000003804
TMSI: F2D4FA0A
Expiration Time: Mon, 07 Dec 2015 09:45:16 +0100
Paging: not paging Requests: 0
Use count: 1show bts, show trx, show lchan, show statistics, …
Now that GSM is working, up to the next challenge!
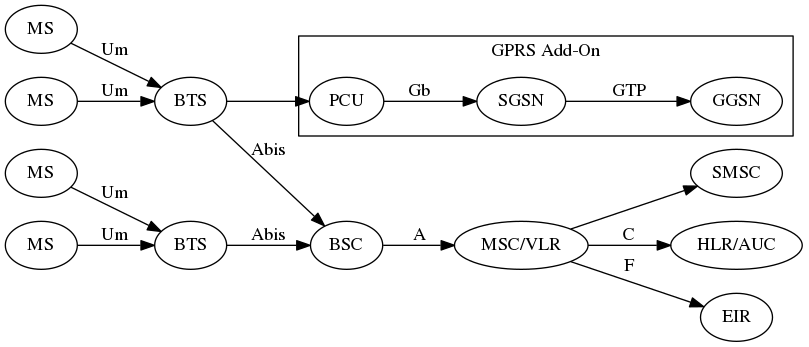
tun device is used for tunnel endpoints
We need to configure those additional components to provide GPRS services.
We assume we have obtained and compiled the osmo-pcu from
git://git.osmocom.org/osmo-pcu
bts 0
gprs mode gprs <1>
gprs nsei 1234 <2>
gprs nsvc 0 nsvci 1234 <3>
gprs nsvc 0 local udp port 23000 <4>
gprs nsvc 0 remote ip 192.168.1.11 <5>
gprs nsvc 0 remote udp port 23000 <6>
enable gprs or egprs mode
NSEI for the NS protocol layer (unique for each PCU in SGSN)
NSVCI for the NS protocol layer (unique for each PCU in SGSN)
UDP port on PCU side of Gb connection
IP address of SGSN side of Gb connection
UDP port on SGSN side of Gb connection
ns
encapsulation udp local-ip 192.168.100.11 <1>
encapsulation udp local-port 23000 <2>
sgsn
gtp local-ip 127.0.0.2 <3>
ggsn 0 remote-ip 127.0.0.1 <4>
ggsn 0 gtp-version 1 <5>
apn * ggsn 0 <6>SGSN-local IP address for Gb connection from PCUs
SGSN-local UDP port number for Gb connection from PCUs
SGSN-local IP address for GTP connection to GGSN
remote IP address for GTP connection to GGSN
GTP protocol version for this GGSN
route all APN names to GGSN 0
OsmoSGSN (still) has no access to the OsmoNITB HLR, thus all IMSIs permitted to use GPRS services need to be explicitly configured.
sgsn
auth-policy closed <1>
imsi-acl add 262778026147135 <2>only allow explicitly authorized/white-listed subscribers
add given IMSI to the white-list of subscribers
In ggsn.cfg we need to set:
listen 172.0.0.1 <1>
net 10.23.24.0/24 <2>
dynip 10.23.42.0/24 <3>
pcodns1 8.8.8.8 <4>IP address to bind GSN to.
network/mask of tun device
pool of dynamic IP addresses allocated to PDP contexts
IP address of DNS server (communicated to MS via signalling)
osmo-pcu, osmo-sgsn, openggsn are running
logging level mm info in SGSN
bsc-nat to introduce NAT-like functionality on A (BSSAP/BSSMAP)
mgw-nat to transparently re-write MAP/ISUP/SCCP